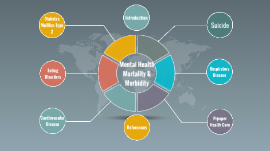
Morbidity and Mortality
Transcript: Guidewire is then withdrawn The trocar is withdrawn. What happened next? 8/8 Started on azithromycin, DuoNebs every 6 hours Solu-Medrol 40 mg every 12 hours, supp O2 as needed NW is a 68 yo female Medical Hx: COPD, GERD, HTN Family Hx: DM and HF in mother Surgical Hx: Tubal ligation (1984) Social Hx: Married, lives at home with husband who takes care of her medications. Tobacco: Former smoker 1 ppd for 50 years, quit in 2005 Allergies: none Medications: Xanax, Paxil, zocor Daliresp (PDE4), Tudorza (LAMA), Pulmicort (steroid), Brovana (LABA), Albuterol (SABA) 8/19 - Nurse Navigator phone encounter Reports that patient will NOT use NIV. Informed that Apria has ordered Nasal Aire NIV appliance that is more like a nasal cannula than a mask which is being shipped directly to patient's home Prior Hospitalizations 4/13/15 - COPD 7/6/15 - COPD 4/22/16 - GI BLEED 5/9/16 - COPD 7/10/16 - COPD Transfer After central line and intubation in ED Pt was transferred to the ICU ABG 8/21 showed acidosis pH 7.22, pCO2 79.5, pO2 302, HCO3 32. Levophed through CVC Titrate per target MAP>65 The Seldinger technique - Sven Ivar Seldinger, was a radiologist from Mora Municipality, Sweden. In 1953, he introduced the Seldinger technique to obtain safe access to blood vessels and other hollow organs. Attempted extubation on 8/26 and reintubated for respiratory distress several hours later despite BIPAP On and off bipap for days Finally extubated on 8/30, placed on bipap A "sheath" or blunt cannula can now be passed over the guidewire into the cavity or vessel. Line was then sutured and dressing applied. It was noted that blood returned from white port, all 3 flush easily. Pressures remained hypotensive during this integral period Pulmonology appointment on 7/20/16 Noted to have advanced COPD and recent admissions for chronic Hypoxemic respiratory failure due to COPD Baseline FEV1 around 26% of predicted. Uses four liter/min oxygen all the time. Patient uses Tudorza , and takes Albuterol as necessary.Patient also uses Advair one inhalation twice a day. Today, she thinks her breathing is back to baseline. Plan Discussed importance of compliance. Continue Tudorza, Pulmicort, Brovana inhalations twice daily Albuterol inhaler six times daily Daliresp once daily Having been in use for a few hours, the patient had received ativan and approx 200cc of Levophed directly into the mediastinum Had some new HF, frequent multifocal PVC's and at one point went to A-FIB for short period of time then went back to SR on her own. Was followed by cardiology 8/11 through 8/17 MSSA growing on sputum cx Remained weak while working with PT Waxing and waning respiratory course Pt continued to refuse BIPAP at night 8/18 - Discharged home w/ home health Prednisone 40 qam x 7 days Pulmicort, Brovana, Turdorza daily Continue round the clock O2 A round-tipped guidewire is then advanced through the lumen of the trocar. A sheath can be used to introduce catheters or other devices to perform endoluminal procedures A case presentation by Mark Haggerty, DO PGY3 Portsmouth Family Medicine The desired vessel or cavity is punctured with a sharp hollow needle called a trocar, with ultrasound guidance if necessary. CT surgery reviewed the images and recommended that it was safe to pull the line Potential areas of improvement and remaining questions Barriers to care Financial - high co-pay on inhalers Unable to tolerate NIV therapy Unwilling to address advanced directives Apparent low motivation, discouraged. Let's get some more background on our patient NW SBT failed on 8/23, 8/24, 8/25 Agitated, pulled out OGT Diarrhea required fecal management system Radiologist talked to ICU regarding CT finding of misplaced CVL Post insertion: All the lumens of the line are aspirated (to ensure that they are all positioned inside the vein) and flushed with either saline or heparin. A chest X-ray may be performed afterwards to confirm that the line is positioned inside the superior vena cava and no pneumothorax was caused inadvertently. Electromagnetic tracking can be used to verify tip placement and provide guidance during insertion, obviating the need for the X-ray afterwards. Sunny day Per pallitaive who had been following; Patient verbalized wanting to shift gears from aggressive measures and focus on comfort. Patient was aware of risk that should she eat by mouth, that it may hasten her death, yet she opted to eat. Comfort care measures initiated by Palliative 9/2 - on prn ativan, fentanyl, robinul, morphine for comfort NW passed away on 9/8/2016 It was noted by nursing that no blood could be aspirated from the ports, and that when the CT finding was noted, the levophed was stopped and no change in blood pressure resulted ED 8/21 Per Medic: alert initially, given solumedrol 125 mg IV, duoneb. Enroute to hospital, patient became more unresponsive, on CPAP Per Husband: She has been SOB since being discharged on 8/18. Per ED nurse: Grayish discoloration of the skin, agonal breathing